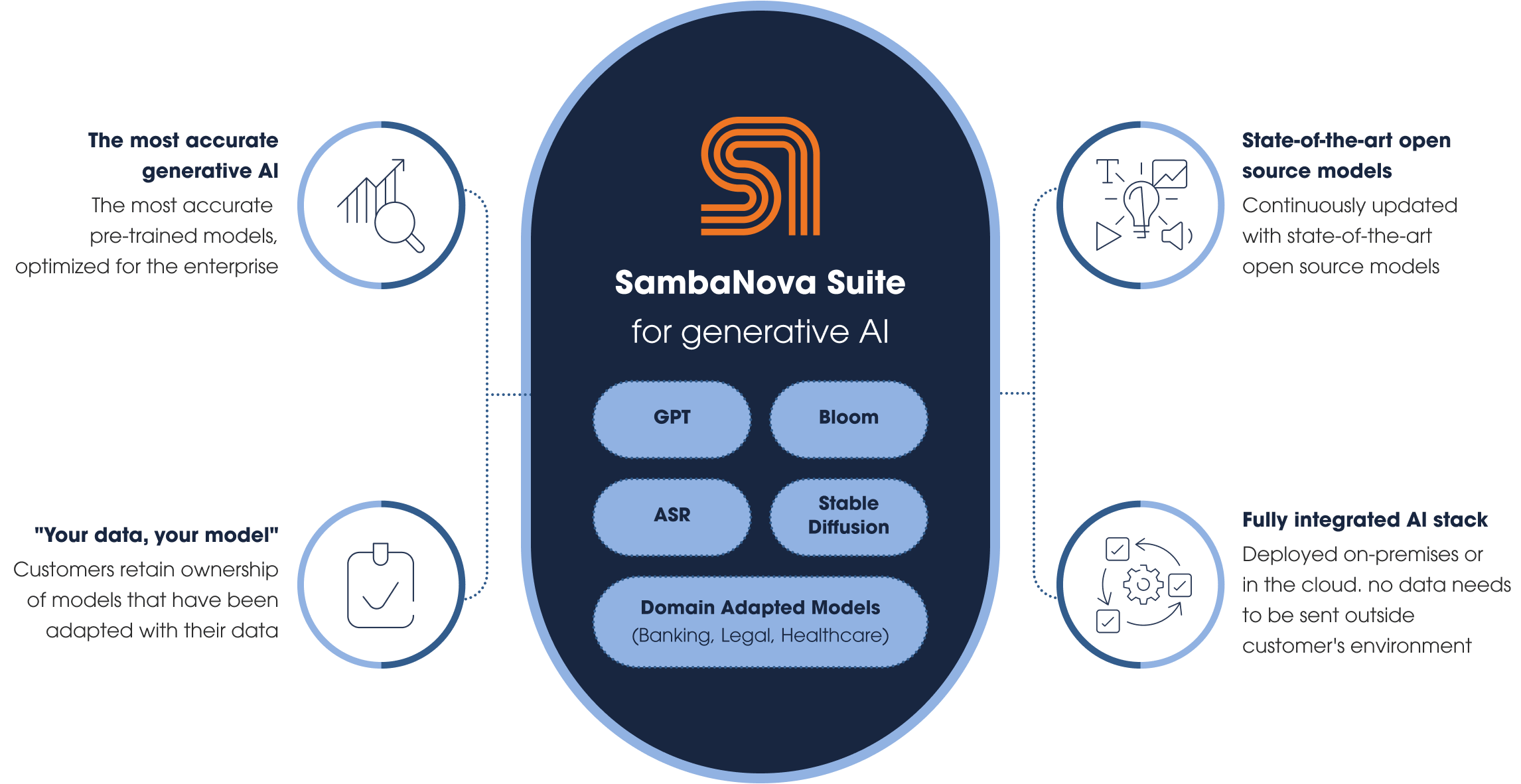
SambaNova’s announcement of Samba-1 marks a significant step in the company’s efforts to provide enterprise customers with a powerful AI solution tailored for a range of tasks, including text rewriting, coding, and language translation. The architecture, described as a “composition of experts,” encompasses a suite of 56 generative open-source AI models.
According to Rodrigo Liang, SambaNova’s CEO, Samba-1 offers companies the flexibility to address multiple AI use cases while mitigating the challenges associated with implementing AI systems in an ad hoc manner. The modularity of Samba-1 enables companies to seamlessly integrate new models into their existing infrastructure without rendering previous investments obsolete. Additionally, its iterative and extensible nature facilitates easy updates, providing customers with the agility to adapt to evolving AI models seamlessly.
By offering a comprehensive solution that combines a diverse set of AI models within a single platform, SambaNova aims to empower enterprises to leverage cutting-edge AI technologies effectively, driving innovation and efficiency across various domains. As the demand for AI solutions continues to grow in the enterprise sector, Samba-1 represents a compelling option for organizations seeking to harness the power of AI to enhance their operations and achieve their business objectives.
Samba-1’s approach presents a unique advantage over other AI systems, including models from OpenAI, particularly in its flexibility and control over routing requests. Unlike single large models such as GPT-4, which process requests in a linear fashion, Samba-1 comprises a collection of 56 independent models. This allows customers to specify rules and policies for routing requests, enabling more tailored and efficient processing based on the specific requirements of each task.
Moreover, Samba-1’s multi-model architecture offers cost benefits when fine-tuning on customer data. Rather than fine-tuning a single massive model, customers can focus on fine-tuning individual or small groups of models within Samba-1. This targeted approach reduces resource requirements and streamlines the fine-tuning process, ultimately saving time and costs for customers.
Additionally, the multi-model strategy employed by Samba-1 has the potential to enhance response reliability by enabling comparison across models. By comparing responses from multiple models, customers can mitigate issues such as hallucination-driven outputs, thereby improving the overall quality and accuracy of AI-generated responses. Although this comparative analysis may require additional computational resources, it offers a valuable mechanism for ensuring the reliability and robustness of AI-generated outputs.
In summary, while Samba-1 may not necessarily be superior to other AI systems in all use cases, its multi-model architecture and customizable routing capabilities provide distinct advantages that make it well-suited for a range of business tasks, offering customers greater flexibility, efficiency, and control over their AI workflows.










