Harvard and Google Unveil the Most Detailed Brain Map Ever Using AI
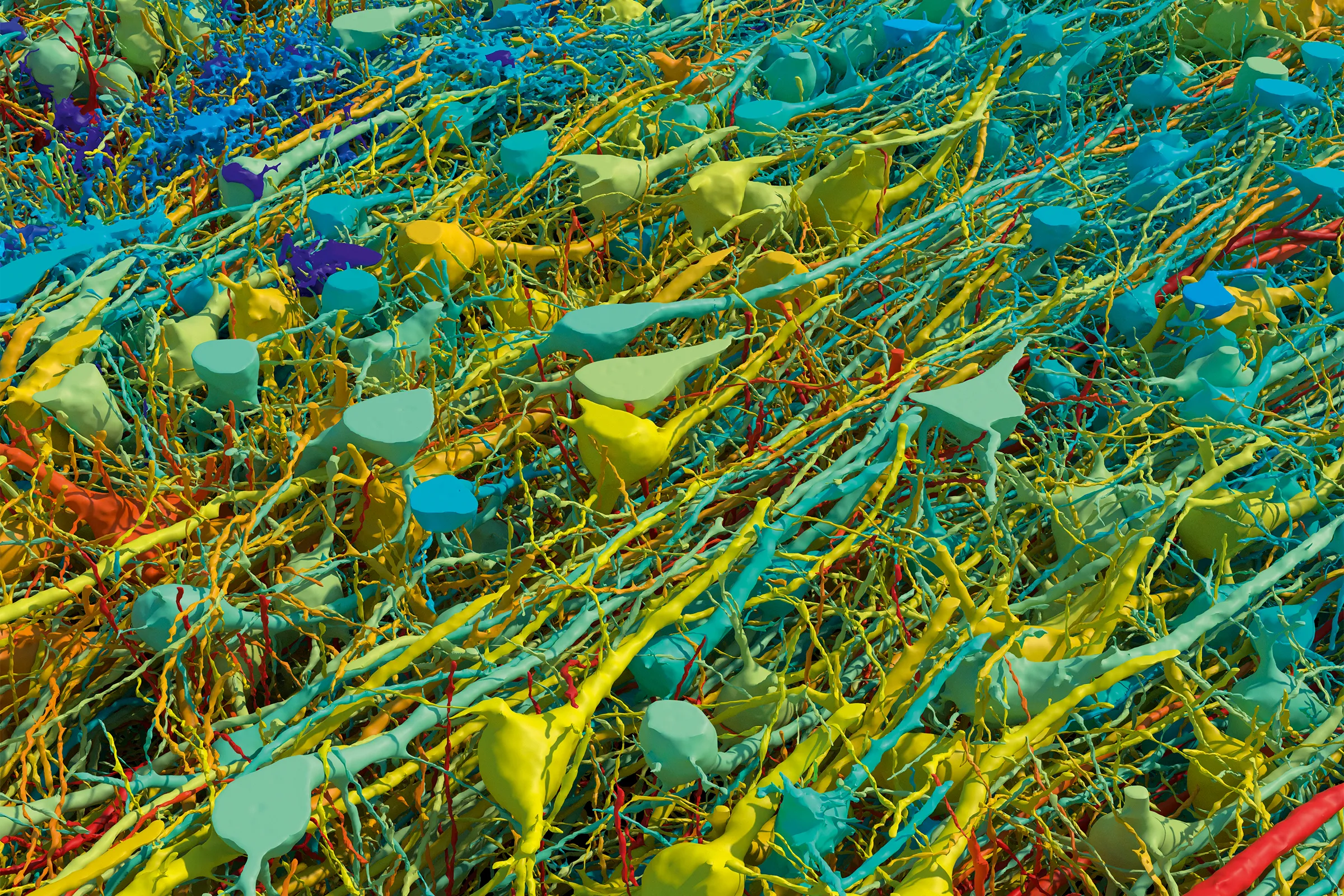
Harvard and Google’s Brain Mapping Breakthrough Reveals Unprecedented Insights into Neural Connections
A groundbreaking project led by Harvard University in collaboration with Google has achieved a milestone in neuroscience by creating the most detailed map of human brain connections ever produced. This ambitious effort centered on a cubic millimeter of the cerebral cortex, which was extracted from a patient during epilepsy surgery in 2014. Over the course of a decade, an interdisciplinary team of biologists and machine-learning experts meticulously analyzed this tiny yet complex tissue sample, which contains approximately 57,000 cells and 150 million synapses. The resulting map provides an unprecedented level of detail, significantly advancing our understanding of the brain’s intricate wiring.
The project employed advanced mapping techniques to tackle the complexity of brain tissue. Initially, the tissue was stained with heavy metals that bind to lipid membranes, making cellular structures visible under an electron microscope. The next step involved embedding the tissue in resin and slicing it into ultra-thin sections, each measuring just 34 nanometers thick. This process transformed the 3D problem of mapping the brain’s structure into a more manageable 2D problem, generating a massive dataset totaling 1.4 petabytes.
To reconstruct the 3D structure from these 2D slices, the team utilized sophisticated machine-learning algorithms developed in collaboration with Google. These algorithms were instrumental in aligning the images and automatically segmenting the different cell types within the tissue. Despite the advanced technology, manual adjustments were necessary to ensure the accuracy and precision of the segmented data. This blend of automated and manual processes highlights the project’s complexity and the innovative solutions employed to overcome technical challenges.
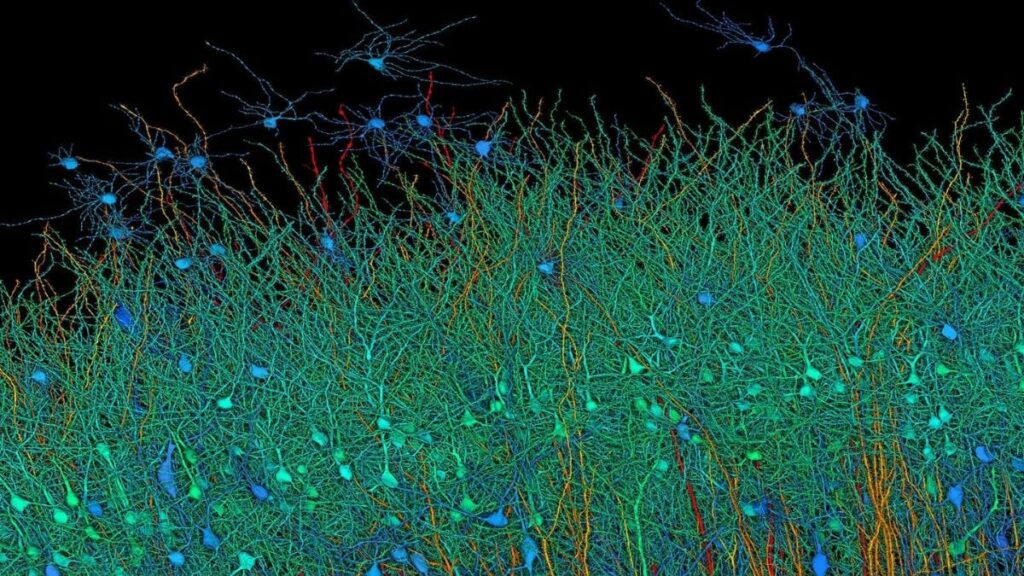
The implications of this detailed brain map are far-reaching. By providing an in-depth view of the brain’s neural connections, the map offers valuable insights into how different brain regions communicate and function. This level of detail is crucial for understanding the brain’s architecture and could pave the way for new discoveries in neuroscience, including insights into neurological disorders and brain function.
In addition to its scientific significance, the project showcases the power of interdisciplinary collaboration between institutions like Harvard and technology companies like Google. The integration of advanced machine learning with traditional biological techniques represents a major leap forward in the field, demonstrating the potential for future innovations in brain research.
Overall, this achievement underscores the importance of combining cutting-edge technology with fundamental scientific research. As the field of neuroscience continues to evolve, projects like this will play a critical role in unraveling the mysteries of the human brain and advancing our knowledge of its complex inner workings.





















